An alpaca-derived nanobody can potently neutralize SARS-CoV-2
Published: 2020-11-27

The COVID-19 research efforts are focused on finding potential targets for future treatments. Research has shown that the affinity of SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD) for ACE2 is considerably higher than that of SARS-CoV-1 which may contribute to pathogenesis. The receptor-engaging part of the spike protein is an attractive target for coronavirus neutralization. A number of conventional neutralizing monoclonal antibodies that bind to RBD have been isolated from convalescent patients. Camelid-derived single domain antibody fragments, also called nanobodies, offer key advantages for specific therapies. Nanobodies are small, easy to clone and express, stable, and cost effective. Previous research has shown that nanobodies can be potent inhibitors of viral infections in vivo, for example respiratory infections.
In a recently published article, an international team of researchers lead by scientists at the Karolinska Institute (first author: Leo Hanke; PIs and corresponding authors: B. Martin Hällberg, Ben Murrell and Gerald M. McInerney) have described the isolation, evaluation, and molecular characterization of an alpaca-derived nanobody, termed Ty1, directed to the RBD of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. The researchers have shown that Ty1 can bind the RBD with high affinity and demonstrated that the monomeric 12.8 kDa Ty1 molecule can potently neutralize a SARS-CoV-2 spike pseudovirus.
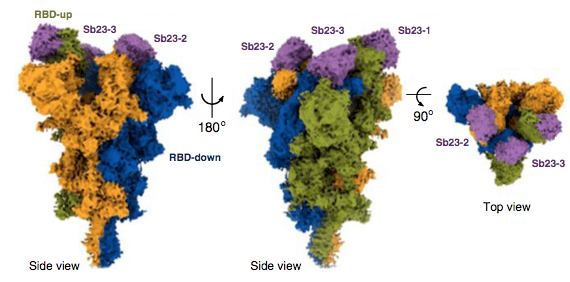
Hanke and colleagues also reported a cryo electron microscopy structure of the spike-nanobody complex at 2.9 Å resolution which shows that Ty1 binds the RBD, sterically hindering RBD-ACE2 binding. In addition, the researchers showed that Ty1 can be expressed in high quantities in bacteria which makes it possible to manufacture it at a large scale. Ty1 is therefore an excellent candidate as an intervention against COVID-19.
To facilitate further research on the potential of Ty1, detailed data has been publicly shared. The researchers have deposited the sequence of Ty1 in the NCBI GenBank sequence database, accession MT784731. ITC data are available on Github. Next generation sequencing data is deposited at the SRA, under BioProject ID PRJNA638614. Jupyter notebooks to reproduce the NGS data processing are available on Github. The cryo-EM density map of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein with Ty1 nanobodies bound are deposited in the Electron Microscopy Data Bank, EMD-11526. The corresponding model was deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB), accession 6ZXN.
Those interested in the behind the paper story can read this blog post by Gerald McInerney.
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement No. 101003653 (CoroNAb), to G.M.M., G.B.K.H., and B.M. and from project grants from the Swedish Research Council to B.M. (2018-02381), B.M.H. (2017-6702 and 2018-3808) and to G.M.M. (2018-03914 and 2018-03843).
Article
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-18174-5
Hanke, L., Vidakovics Perez, L., Sheward, D. J., Das, H., Schulte, T., Moliner-Morro, A., Corcoran, Achour, A., Karlsson Hedestam, G. B., Hällberg, B. M., Murrell, B. & McInerney, G. M. An alpaca nanobody neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 by blocking receptor interaction. Nat Commun, 11, 4420 (2020).