A novel approach to discover and characterize broad-spectrum antivirals
Published: 2020-12-18
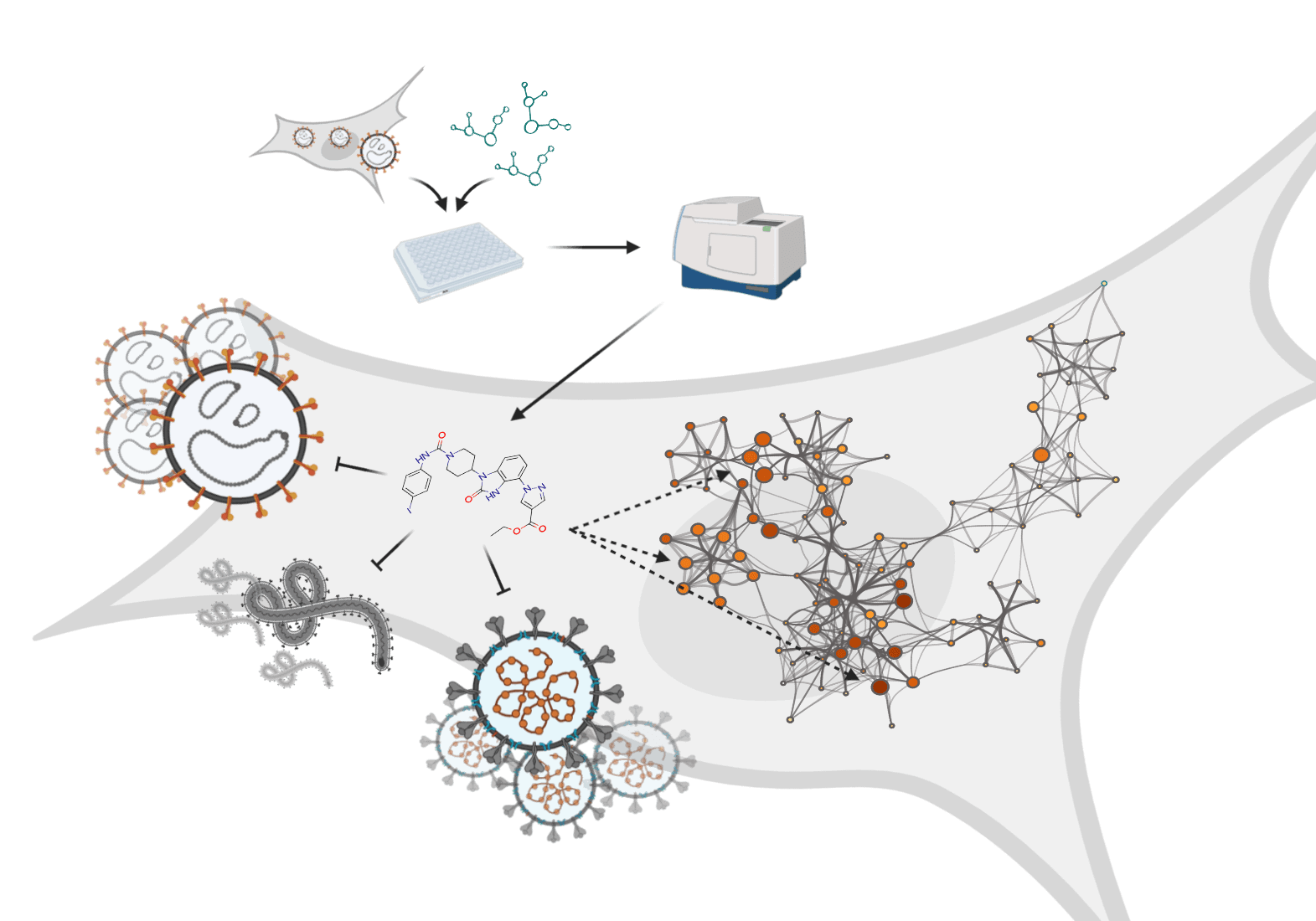
The ongoing pandemic of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has had severe social and economic consequences in many countries. The world has also seen recent serious outbreaks of other RNA viruses like Ebola virus (EBOV) and Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV) in the last decades. New antiviral strategies are therefore urgently needed. Targeting host cell pathways supporting viral replication is one approach to develop antiviral compounds. This could be especially important with new, unexplored viruses with limited information of virus biology.
In recent years technical advances like advanced mass-spectrometry-based target identification method thermal proteome profiling (TPP) has been developed to monitor drug–target interactions in living cells. TPP can measure changes of protein thermal stability when the compound binds to cellular targets and can therefore be used to detect drug targets and changes in cellular pathways.
A collaboration study from the Karolinska Institute led by Marjo-Riitta Puumalainen (first author: Marianna Tampere), recently published in Viruses, presents a strategy to identify host-targeted small molecule inhibitors by using an image-based phenotypic antiviral screening assay followed by extensive target identification efforts revealing altered cellular pathways upon antiviral compound treatment.
The researchers have established an image-based phenotypic high-throughput screening assay coupled with automated image analysis. They have tested a set of in-house inhibitors targeting oxidative stress and nucleotide metabolism pathways and identified two small new molecular inhibitor compounds TH3289 and TH6744 that have antiviral activity. Both compounds TH3289 and TH6744 reduced the non-pathogenic Hazara virus titer to similar effect at 10-fold lower dose as marketed antiviral drug Ribavirin. In addition, the newly identified compound TH3289 had antiviral activity on cell lines infected with pathogenic viruses, SARS-CoV-2, EBOV, and CCHFV, respectively. Lastly, Tampere and colleagues studied the pharmacological activity of the new antiviral compounds using TPP, and they were shown to be involved in cellular HSP70 pathways. In summary, the authors concluded that combining phenotypic screening with a recently developed target identification methods could have a great potential for future antiviral drug discovery and reveal new host cell-virus biology.
The authors have shared part of the data supporting their findings openly in the article Supplementary Materials and part in the SciLifeLab Data Repository (hosted by FigShare) under DOI 10.17044/scilifelab.13089023. The raw mass spectrometry data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD021494.
This project has received funding from the Swedish Research Council (2017-05631 for T.H., 2015-00162 for T.H. and 2017-01653 for R.J.), the European Research Council (ERC-2016-PoC 755150 for T.H.) and the Swedish Childhood Cancer Foundation (TJ2016-0035 and PR2016-0019 for R.J.). M.-R.P. was supported by Swiss National Foundation Fellowship (P2ZHP3_158770) and an EMBO Long-Term Fellowship (ALTF-1140-2015). M.T. was supported by SSF (FID15-0010). This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement no 722729.
Article
DOI: 10.3390/v12121423
Tampere, M., Pettke, A., Salata, C., Wallner, O., Koolmeister, T., Cazares-Körner, A., Visnes, T., Hesselman, M.C., Kunold, E., Wiita, E., Kalderén, C., Lightowler, M., Jemth, A.-S., Lehtiö, J., Rosenquist, Å., Warpman-Berglund, U., Helleday, T., Mirazimi, A., Jafari, R., & Puumalainen, M.-R. Novel Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Inhibitors Targeting Host Factors Essential for Replication of Pathogenic RNA Viruses. Viruses, 12 (12), 1423 (2020).